Inventions and Discoveries
Today, in the world, inventions and technological progress are very fast
But in the past, people spent years to make different tools
These inventions, which were meant to make things easier and were very useful in the progress of humans in various fields, because they were the most basic tools and equipments, have been developed by different civilizations over hundreds of years.
However, many of the same distorters of history, most of whom are racists and ethnocentrists, have attributed these inventions and innovations to the Turkish race.
14 inventions attributed to Turks
1. The invention of the carpet

The first discovered carpet called Pazilik carpet
Pazilik carpet is the oldest carpet in the world, which was dug in the years 1326 to 1947 (1949-1947) by Sergei Rodenko, a Russian archaeologist, in the Pazilik Valley, located at the beginning of the Altai Mountains in Russia, next to famous ancient objects such as wooden vases, mummies, carvings.
Horse riding along with other artifacts were discovered in the frozen tomb of one of the Scythian rulers
2. Invention of the wheel

A wheel is a round tool that has various uses; But its first and most important use is to reduce friction and facilitate movement. The wheel is one of the most important human inventions that was made in the 4th millennium BC in the ancient land of Sumer.
Sometimes the credit of the first image of wheeled vehicles is given to the Halaf culture in the years 6500 to 5100 BC, but this is doubtful as there is no evidence that the Halafians used wheeled vehicles or even pottery wheels.
3. The invention of eating utensils such as plates, spoons, forks and pots
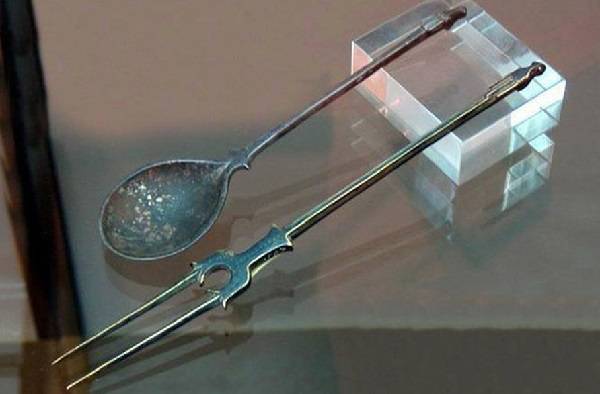
A spoon is a small metal or wooden tool that has a handle and is used to place food and eat it. Usually, a spoon is used to eat liquid, semi-liquid, or grainy foods (such as rice) that are difficult to eat with a fork.
A spoon is also used in cooking and for adding ingredients or measuring them.
A spoon is used to eat different foods.
Spoon is a word with Turkish roots, but the Pahlavi culture of selling spoon considers the word spoon to mean the old Persian word Kafchak. Its Persian equivalent is kafchak, which survived from Middle Persian kafčak.
In other Iranian languages, such as Kurdish "kauchek", Lori "kamche", Talshi "keche", and in Gilki and Mazni, kache is found. It is believed that this word is related to the word kafgir. The word "Liz shoe" is also a derivative of this word
A fork is a tool with a handle that has three or four teeth. The material of this device is metal, plastic or wood. Fork in Persian also means a person's claw that is slightly bent.
There is no exact information available about the history of the invention of the fork, but this device was not common in Europe until the 10th century AD.
4. Inventing or devising various dishes such as Qorme Sabzi, Dol Meh and Abgosht bozbash ...
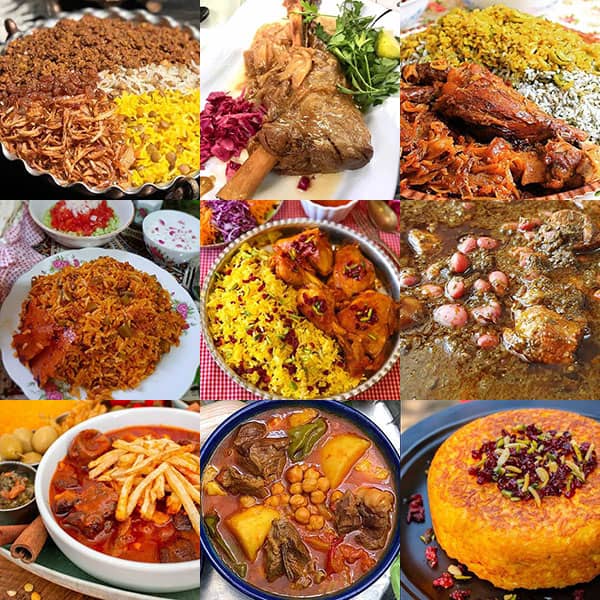

It is food or food that is prepared for consumption in different societies in raw and untouched, modified or semi-modified form. Food can be of animal or vegetable (or sometimes mineral) origin, and it is consumed to meet the need for nutrition.
In the past, food gathering was done by hunting or picking fruits, but today it is mostly prepared by using the skills of agriculture, animal husbandry and fishing.
Eating habits are different in different cultures.
Most communities have special customs for cooking and their food preferences according to their traditions and customs. Many cultures have diversified their foods by preparation methods, cooking methods, and food preparation.
5. Line invention

Calligraphy, scribe or linguistic or writing system, is an art or a means to record and write thoughts using signs that are familiar to the eye and can be seen. Jahiz says: calligraphy is the language of the hand, the protector of thoughts and works.
The invention of calligraphy dates back to about 6,000 years ago in Mesopotamia, which was located between the Tigris and the Euphrates. The Sumerians were the first to discover writing.
They wrote with small pictures as calligraphy marks that they carved on clay plates. These small pictures for writing have been seen in the ancient works of other countries such as China and Egypt, but at first it was the invention of the Sumerians and finally these small pictures created cuneiform.
The writings created with these images carved on the flowers can only be read by experts and professional calligraphers.
In the ancient world, we come across four types of thinkers as follows:
Chinese script
Cuneiform
Egyptian hieroglyphic script
Phoenician line
6. Inventing a calendar using the names of animals instead of the names of the moon or constellation

The beginning of the calendar is the beginning of the historical period and human social life and agriculture and his need to determine the timing of agriculture. The lunar calendar using the moon is the first written human calendar. Then the solar-lunar calendar and then the solar calendar are used.
The history of calendar use reaches 30,000 years.
From 4241 BC, the Egyptians were the first nations to use the 365-day solar calendar, and the Babylonians were the first nations to define the year based on twelve 30-day months. After a few years, the Babylonians would add one or more months to their calendar whenever they realized that the difference in their calendar was increased by four seasons. Its relatively evolved form was an extra month every six years. Julius Caesar introduced the Julian calendar in 45 BC at the suggestion of Greek astronomy.
This calendar was based on the solar year with a length of 365.25 days. The year was 365 days, and to compensate for the day's deficit, one day was added to the length of the year every four years (leap year).
From then on, the Christian Gregorian calendar was derived from the Gregorian calendar, which was later refined by the Gregorian calendar.
After that, the most accurate calendar was created in calculating the exact fraction of the year of the Iranian Jalali calendar (471 lunar year / 1079 AD), which today is the solar Hijri calendar derived from it and its continuation in calculations. The oldest Iranian calendar is the 365-day Persian calendar with its origin in 5025 BC, which was similar to the ancient Egyptian calendar.
The religious calendar of Muslims and Jews is lunar.
7. Metal discovery

Nearly 10,000 years have passed since the first metal discovered by mankind. Copper is the first metal discovered by humans, which still plays an important role in human life after thousands of years. Copper is one of the rarest metals that exists in free form in nature.
These characteristics made the Neolithic man replace this metal with hard stone very soon. Archaeological research has not yet been able to clearly and decisively announce the initial location of the first discovered metal.
But the documents indicate that the signs of copper use have been attributed to 8 thousand years BC in the region of Asia Minor and Mesopotamia. Archaeologists know that these places are the places where the first human civilizations were formed.
The remarkable point in this context is that Iranians have been using copper for many years. The proof of this claim is the existence of old and primitive furnaces in the remains of that era, although these furnaces are very primitive.
In addition, the copper objects discovered in Hill Silk, Hill Zaghe, Tel Iblis indicate the fact that Iranians used copper to make objects about 5 thousand years ago.
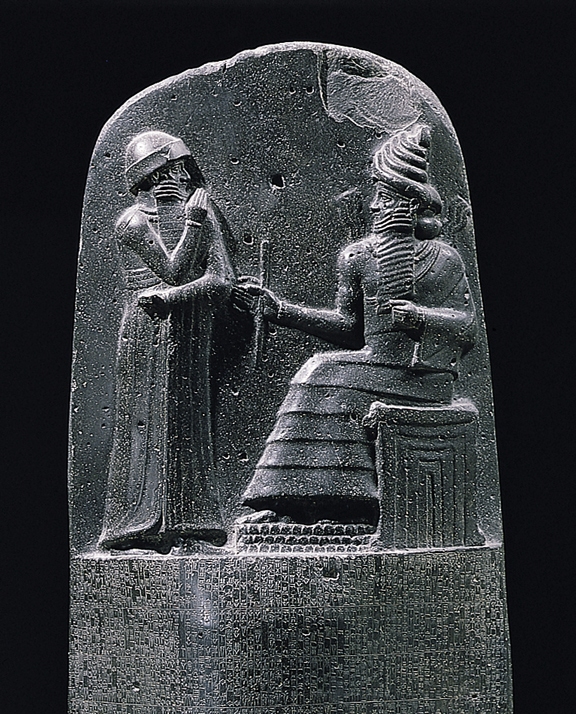
8. Inventing the Seneca tablet for writing laws (referring to Hammurabi's tablet)
Hammurabi tablet related to Babylonian civilization
The Code of Hammurabi, which was written by the order of Hammurabi, the king of Babylon, contains 282 articles on criminal law, civil law, and business law. The column on which Hammurabi's laws are engraved is made of basalt and is about 2.5 meters high. The text of the rules surrounding this column is written in cuneiform in 34 rows.
The Code of Hammurabi is the first known document in which a ruler publicly announces a complete set of laws for his nation.
Hammurabi (1810-1750 BC) is the sixth king of the first dynasty of the kings of the ancient country of Babylon. His royal history (1750-1792 AD) is given. This law includes the rights and relationships of people with each other based on the important economic factors of that time. Hammurabi said that the tablet of his laws was revealed to him by Marduk.
9. Invention of the clock and divisions of the day and night

The history of time tools talks about the tools that were used to measure time, such as the blue clock and...
Kariz Zibad Gonabad Blue Clock
One of the first instruments for measuring time was the blue clock, which is believed to have been invented in Egypt. Signs of using tools to measure time have been observed since about 4,000 years ago. In Egypt, Iran, Iraq, India and ancient civilizations, tools have been found that archaeologists say were used to measure time. However, according to most researchers, these tools were not used to measure time, but were more religious and religious and for religious occasions.
Today, the time measuring device is called a clock, which is the most important tool for measuring time. The clock in its new form (24 hours) became popular from the 15th century and has become popular in the last century.
In the past, various tools have been used to calculate time:
Sun clock
Hourglass or hourglass
blue hour
candle clock
With the progress of science and human knowledge, gradually, more accurate mechanical, weight, spring, electric, battery and computer clocks replaced water clocks, sun clocks and sand clocks.
10. Discover the angle and divide it into 360 degrees
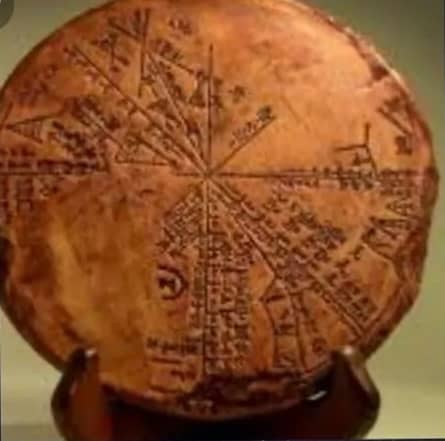

Babylonian mathematics, which is also called Assyrian-Babylonian mathematics, is a mathematics that was used and spread among the people of Mesopotamia from the first days of Sumerian rule until the fall of Babylon in 539 BC.
Babylonian mathematical writings are abundant and well edited. Babylonian mathematics can be divided into two parts from a chronological point of view, the first is the ancient Babylonian period (from 1830 to 1531 BC) and the second is more related to the Seleucid period around three to four centuries BC. From the point of view of the content, no obvious difference can be seen between the two periods, therefore, it can be said that Babylonian mathematics had a stable state for nearly two thousand years.
Our data about Babylonian mathematical knowledge is obtained from nearly 400 clay tablets that were pulled out from under the soil. These tablets are cuneiform, written on while the clay was still wet and then dried in the sun or in an oven. The topics presented in these essays are: fractions, algebra, quadratic and quadratic equations and Pythagorean theorem.
In one of these manuscripts, an approximation for 2 {\displaystyle {\sqrt {2}}} {\sqrt {2}} was provided, which was accurate to three digits in base 60 (equal to 7 digits in base ten)
Basic 60 number system in Babylonian mathematics
Babylonian mathematics is a collection of numbers and more advanced mathematical endeavors in the ancient Near East, written in cursive.
. Since the data related to the ancient Babylonian period (the first period of Babylonian mathematics) is more abundant at the beginning of the second millennium BC, most of the historiographical researches have focused on this period. However, there is a debate on the main roots of Babylonian mathematics, some archaeologists believe that the beginning of Babylonian mathematics goes back to the fifth and third millennia BC, because clay tools with the use of counting and clay were found as old as 5000 years BC.
Babylonian mathematics was primarily written in cuneiform and in Akkadian and Sumerian languages. The Babylonian number system was based on 60
The ancient Sumerians of Mesopotamia developed a complex system of metrology from 3000 BC. Since 2600 BC, they have left writings on problems related to multiplication, division and geometry. It can also be said that some signs related to Babylonian mathematical knowledge go back to this period.
11. The invention of accounting and its application in the administration of the country

Accounting dates back thousands of years and can be traced back to ancient civilizations. The initial development of accounting dates back to ancient Mesopotamia and is closely related to the development of writing, counting and money.
There is also evidence of early forms of bookkeeping in ancient Iran and early auditing systems by the ancient Egyptians and Babylonians.
By the time of Emperor Augustus, the Roman government had access to detailed financial information.
12. Inventing architecture and building ziggurats that were built in different civilizations and parts of the world such as Sumer and Elam and...
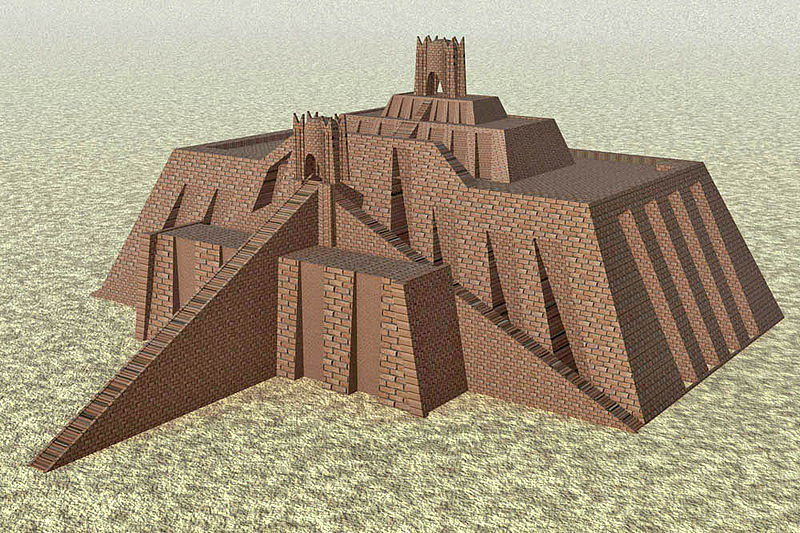

Pre-Parsi style of architecture is a sub-style of architecture (or sub-style) in Iranian architecture.
This style of architecture flourished in the Iranian plateau until the 8th century BC during the Median Empire. This style is often classified as a subset of the Persian style.
The Zagheh hill near Qazvin is the oldest surviving work of this architectural style. Other prominent examples of this style are: Chaghazanbil, Hill Silk, Burnt City and Hegmataneh.
Elamite buildings are under this style.
13. Inventing and making musical instruments such as harp, tar, tonbak, balan, etc.
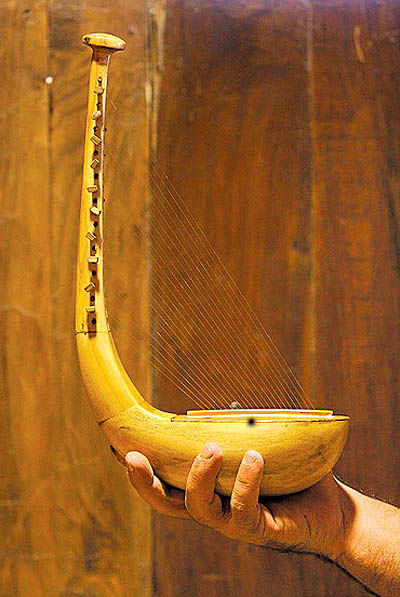

An instrument is a musical instrument.
Although any device that makes sound can be considered an instrument, but in this article, an instrument refers to an instrument that is made solely for playing music.
Probably the oldest means of producing music is the human voice. After that, perhaps all kinds of percussion instruments and after that wind instruments are older. A piece of pierced bone from the Neanderthal period is considered to be the oldest wind instrument discovered.
Iranian musical instruments such as rebab, barbat, tanbur, tambourine, organ, harp, sernai, trumpet and chaghana are three thousand years old.
This flute, found in Slovenia, is believed to be the oldest musical instrument found in the world, with a history of 50,000 to 60,000 years.
The instruments made in Iran are divided into stringed, wind and percussion instruments in terms of how they produce sound, and they are also classified into 3 groups of metal, clay and wooden instruments, among which wood has played a more prominent role. The wood, log and trunk of the mulberry tree is the most used in making Iranian instruments.
Horns of animals such as rams, lamb skins, oysters from the North and South seas, and the bones of camels have been used in a limited way in making instruments. Also, in a small number of instruments, such as the dozele instrument, it is made from the leg bone of a fish-eating chicken.

_(9420310527).jpg)




